Evaluation of the inflammatory predictive efficiency of progranulin as compared with common pro-inflammatory regulators
Abstract
Progranulin (PGRN), is a multifunctional protein with profound expression in epithelial and immune cells in which plays a crucial role in controlling host-defense signaling pathways during infection and inflammation. The current study was carried out to evaluate the efficiency of PGRN as a predictive inflammatory marker for a group of diseases with different etiologies that cause acute and chronic inflammations. A total of 120 participants with various diseases including rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Helicobacter pylori infection, burn wound, hepatitis B, and prostate cancer, and 20 healthy people were enrolled in this study. The levels of serum PGRN and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were detected. Elevated serum PGRN levels have been reported in all patient groups when compared with those in healthy controls (P > 0.05). Likewise, increased serum hsCRP and IL-6 levels were seen in all patient groups. However, for some patient groups, the differences in hsCRP and IL-6 levels did not reach statistical significance (P > 0.05) in comparison with control group. Furthermore, serum PGRN levels exhibited positive correlation with hsCRP in H. pylori and RA patient groups. As well as, with IL-6 only in RA patient group, whereas no significant correlations were found with the rest of studied diseases. This study concluded that PGRN is an effective nonspecific inflammatory indicator of acute and chronic inflammations. It had also a higher predictive efficiency than hsCRP and IL-6 which are commonly used as inflammatory predictive markers.
INTRODUCTION
Inflammation is a defense mechanism that involves immune cells, blood vessels, and chemical mediators in the intricate biological reaction of body tissues to deleterious stimuli like pathogens, damaged cells, or irritants [1]. Many diseases, such as cancer, rheumatoid arthritis, infection, burn injury and gastrointestinal disease, all have inflammation as a common etiology [2-5]. Although the specifics of the initial stimulus and its location within the body determine how the inflammatory response processes are carried out, they all share a common mechanism that involves the recognition of harmful stimuli by cell surface pattern receptors, activation of inflammatory pathways, liberation of inflammatory markers, and attraction of inflammatory cells [6]. The immune system performs a number of important tasks, including preventing the invasion of harmful microbes, eliminating mutant somatic cells, and regulating the level of immune response to antigenic stimuli [7]. In connection to physiological and pathological situations, the immune system is inextricably linked to alterations in inflammatory pathways. However, unmanaged inflammatory reactions and persistent immunological responses may cause immune system illnesses such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), multiple sclerosis (MS) and type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) [8]. PGRN, a secretory glycoprotein with 593 amino acid remnants, has been found to be present in a variety of tissues, including epithelia, cell lines derived from myeloid and lymphoid tissues, bone marrow, and solid organs. It is a critical actor and regulator of numerous system activities [7]. It involved in cancer, tissue repair, embryonic development, and wound healing [9, 10]. PGRN is also crucial for controlling inflammation by directly interacting with the tumor-necrosis-factor receptors (TNFR1, TNFR2 and DR3) and blocking the TNF-mediated inflammatory signaling cascade [11]. Elevated serum PGRN levels are recently linked to systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and RA [12]. This finding implied that PGRN played a key role in modulating the inflammatory process and mediating its anti-inflammatory effects, therefore the goal of the present study was to assess the efficiency of PGRN as a predictive inflammatory marker for a group of diseases with various etiologies that lead to acute and chronic inflammations.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Study participants
Between March 2022 and July 2022, 120 participants with various diseases (20 with RA, 20 with H. pylori infection, 20 with burn wound, 30 patients with hepatitis B and 30 patients with prostate cancer) in addition to 20 apparently healthy people, as controls, were enrolled in this study.
The study methodology was confirmed by the ethics committee of Pharmacy College, Basrah University, Iraq, according to the document number (7/40/1011). As well as all participants provided a verbal consent.
Sample collection and laboratory measurements
A blood sample of 5 ml was collected from all participants using venipuncture with aseptic precautions. After centrifugation, sera were separated and stored at −20°C until utilized in subsequent assays. Serum PGRN concentrations were measured by Sandwich ELISA technique using (Hu PGRN ELISA kit, MyBioSource, USA). Likewise, the Double Antibody Sandwich ELISA technique was employed to qualify serum IL-6 concentrations utilizing Hu IL-6 ELISA kit (MyBioSource, USA). PGRN and IL-6 analyses were performed using a Thermo Scientific microplate reader (Multiskan FC-USA) at 450nm.
The hs-CRP concentrations were measured on Abbott’s Architect c4000 analyzer by CMIA technique using Abbott’s FDA-approved kit (Multiagent CRP Vario). Furthermore, CMIA technique using Architect (Abbott-USA) was utilized for detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide (Anti-CCP), prostate specific antigen (PSA) and procalcitonin concentration. VIDAS® H. pylori IgG test (BioMérieux/ France) was used for detection of anti-Helicobacter pylori IgG antibodies in patients’ sera by enzyme-linked fluorescence assay (ELFA) technique to confirm the infection with H. pylori. All tests were carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was carried out using SPSS (Statistical Package of Social Science) software. The independent t test, Mann-Whitney U test, and person's correlation were used to compare the differences between the patient groups and control group. Data are reported as the mean ± standard deviation and a P value of less than 0.05 (P < 0.05) was deemed to be statistically significant.
RESULTS
Demographic profile of participants
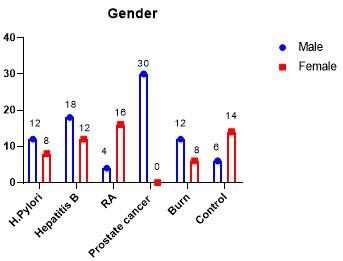
The distribution of patient groups as well as control group according to gender have been represented in Figure 1. Males were predominating in all patient groups except in RA. Regarding the age of patients, they were ranged between 38-65, 37-62, 47-63, 27-77 and 2-45 years old in patient groups of H. pylori, hepatitis B, RA, prostate cancer and burn wound, respectively. While in healthy group, the range of age was 17-55 years old.
Levels of serological parameters in patients
Serological tests that approved to diagnose patients within this study were IgG (IU/ml), HBs-Ag (S/CO), Anti-CCP(IU/ml), PSA (ng/ml) and procalcitonin (ng/ml) for confirming of H. pylori infection, hepatitis B, RA, prostate cancer and burn wound, respectively (Table 1).
Table 1. Confirmative laboratory tests in different patient groups.
Levels of serum PRGN, hsCRP, and IL-6 in patients
Serum PGRN levels were evidently greater (P < 0.05) in patients with H. pylori, hepatitis B, RA, prostate cancer and burn wound than in healthy controls (14.96±1.75, 14.22±1.43, 12.60±3.23, 13.19±1.99 and 13.17±1.59, respectively vs 1.29±0.36 ng/ml) (Table 2; Figure 2). On the other hand, serum hsCRP levels were also found to be comparable, patients with H. pylori, RA, prostate cancer and patients with burn wound had significantly higher (P > 0.05) mean hsCRP level than control group (1.61±2.04, 4.462±5.29, 3.33±3.43 and 6.07±3.60 respectively vs 0.22±0.15 mg/dl). Whereas statistically non-significant variation (p = 0.109) was found in the patient group of hepatitis B in comparison with healthy group (0.96±1.67vs 0.22±0.15 mg/dl) (Table 3; Figure 3).
Moreover, serum IL-6 levels were considerably higher (P < 0.05) in the patient groups of hepatitis B, RA, prostate cancer and burn wound as compared with healthy controls (13.23±5.51, 17.62±12.49, 14.14±8.09 and 25.52±15.81 respectively vs 7.89±1.846 pg/ml). While statistically non-significant variations (P = 0.890) were observed between patients infected with H. pylori and control group (9.82±5.49 vs 7.89±1.84 pg/ml) (Table 4; Figure 4).
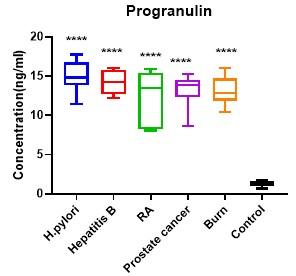
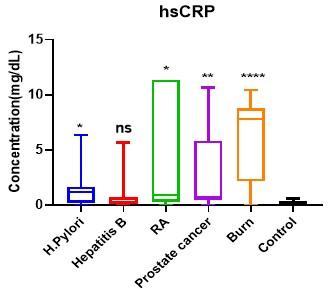
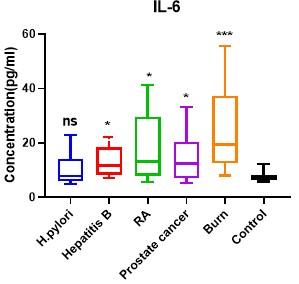
Table 2. Differences in serum progranulin levels between patient and the control group.
Table 3. Differences in serum hsCRP levels between patient groups and the control group.
Table 4. Differences in serum IL-6 levels between patient groups and the control group.
Correlation between PRGN and other inflammatory biomarkers
In order to identify the efficiency of PGRN in predicting inflammations, it was necessary to analyze the correlation between serum level of PGRN and common inflammatory biomarkers (hsCRP and IL-6). Table 5 revealed that PGRN levels exhibited positive correlation with hsCRP levels in H. pylori group (r = 0.520; P = 0.047) and in RA group (r = 0.772, P = 0.042). However, no significant correlations were observed between those two inflammatory markers in hepatitis B, prostate cancer and burn wound groups (r = -0.453, P = 0.090; r = 0.182, P = 0.517; r = 0.155, P = 0.582 respectively). In addition, PGRN levels were shown to be strongly associated with IL-6 only in RA patient group (r = 0.763, P = 0.046), whereas no important correlations were shown in the rest of studied diseases.
Table 5. Correlations between serum PGRN and common inflammatory biomarkers in different patient groups.
DISCUSSION
PGRN is an essential mediator of inflammatory and immune reactions [13]. It has been recently suggested that PGRN's anti-inflammatory properties contribute to a number of inflammatory diseases [14], hence the objective of this study was to assess the efficiency of PGRN as a predictive inflammatory marker in comparison with common pro-inflammatory regulators. For this purpose, PGRN serum levels were estimated in patients with H. pylori, hepatitis B, RA, prostate cancer and burn wound.
Regardless to the gender and age, a significant elevation in serum PGRN levels was observed in all studied patient groups compared to those in control group. In line with the findings of current study, several studies indicated that circulating PGRN levels are increased in a variety of illnesses, including renal disease [15, 16], type 2 diabetes [17], cancer [18], COVID19 disease [19] and RA [20].
H. pylori infects more than half of the world's population, and it has been classified by the WHO as a group 1 carcinogen [21]. PGRN expression was greatly increased in gastric epithelial cells after infection with H. pylori. However, it is still unclear whether increased production of PGRN represent a protective response to eradicate H. pylori infection or it constitutes an adaptive response of the gastric epithelial cells [22]. Ren et al. identified a probable method by which PGRN exerts a significant influence on H. pylori infection and showed that H. pylori infection increased the expression of PGRN, which in turn regulated the expression of CDK4, a target gene of PGRN, via activating the phosphatidylinositol 3 kinases/protein kinase B (PI3K/AKT) signal pathway to competitively interfere with activation of TNF-α mediated inflammatory cascade [23].
On the other hand, when Gong et al. looked into the clinical significance of circulating PGRN in individuals with chronic hepatitis B, they observed that these individuals had significantly higher serum levels of PGRN than healthy individuals, indicating that PGRN plays an effective role in the pathogenesis of hepatitis B. [24].
Furthermore, Zhao et al. reported that PGRN participates in the progression of associated immunological illnesses that affect joints or arthritis complications like RA by acting as a potent stimulator in response to cartilage differentiation [25]. In 2014, Yamamoto and colleagues used ELISA to quantify the serum PGRN levels of patients with RA and observed a remarkable rise in PGRN levels when compared to controls which were not influenced by sex or age. As well as, they showed that the serum PGRN could be a valuable tool for tracking the progression of the disease in RA patients [26]. Likewise, Cerezo et al. showed elevated PGRN expression at localized inflammation and suggested a connection between PGRN levels, illness activity and functional impairment in RA patients [20].
Regarding the PGRN in cancer, previous studies have reported significant biological effects of PGRN on several cancer types. It was found to regulate the carcinogenesis due to its enhancement of cell growth, migration, invasion, angiogenesis, malignant transformation, resistance to anticancer medications, and immune avoidance [27]. Multiple human cancers, including those of the breast, ovarian, endometrium, cervix, liver, kidney, prostate, and brain, have been associated with elevated PGRN levels, where PGRN works as an autocrine growth factor by regulating the motility and invasion of transformed cells [28]. In breast cancer, glioblastoma, and ovarian cancer, high PGRN expression levels have been associated with an aggressive phenotype and a bad prognosis [18, 29]. Otherwise, Monami et al. sided with the hypothesis that PGRN might be critical in the progression of prostate cancer than in its initiation [30]. In a study of serum PGRN levels in men with prostate cancer, Greither et al. found that the levels are significantly different between healthy individuals and patients with prostate cancer [31]. The level was also correlated to the age and the prognosis of patients, with younger patients (≤66 years), had a significantly better overall survival than elder patients [31].
Moreover, inflammation and injury cause PGRN to be strongly expressed. Burn damage/ wound healing is a coordinated cell process including cytokines and regulatory growth factors [32]. According to a previous study, PGRN caused a greater buildup of fibroblasts, blood vessels, neutrophils, and macrophages in the wound. It stimulates cell division, migration, and the development of tubules resembling capillaries by directly influencing isolated dermal fibroblasts and endothelial cells. Consequently, PGRN is likely a growth factor related to wounds [33].
In this study, although the serum levels of PGRN, IL-6 and hsCRP were increased in all patient groups, correlation serum levels of PGRN with the traditional biomarkers (hsCRP and IL-6) exhibited positive correlation only with hsCRP in H. pylori and RA patient groups, as well as with IL-6 in RA patient group, while no significant correlations were found with the rest of studied diseases. In general, inflammatory biomarkers serve as measures of the immune system's health, increased their levels may support evidence of ongoing illness processes and generate snapshots of complicated immune responses to the environment of acute and chronic inflammations. Limited or no prior data are available regarding correlations between PGRN and different inflammatory biomarkers in acute and chronic inflammations such as those included in the current study. According to Cerezo et al., there was no correlation between serum PGRN levels and CRP levels in RA [20]. Meanwhile, Baillet et al. studied 813 RA patients and concluded that IL-6 and CRP were strongly correlated [34]. IL-6 is rapidly produced during immunological responses to infection and tissue damage, and the uncontrolled expression of IL6 exerts a pathological impact on autoimmune disease and chronic inflammation [35]. On the other hand, a study by Feng et al. [36] revealed that in the critically ill patients, the CRP serum levels elevated as the clinical picture deteriorated and reached a significant difference. Therefore, in patients with RA, the increased levels of PGRN that positively correlated with both hsCRP levels and IL-6 levels may predicting poor outcomes.
CONCLUSIONS
The results of the current study suggested that PGRN is an effective nonspecific inflammatory indicator of acute and chronic inflammations that resulted from different etiologies. It had also a higher predictive effect than hsCRP and IL-6 which are commonly used as inflammatory predictive markers. This study provided updated information to guide future studies. It is recommended that such studies with a larger sample size should be carried out to establish the role of PGRN as a marker for the prediction of inflammations and their sequels.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
None.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
NWM and ZNE contributed to the design of the study. OAN and ZNE carried out the laboratory measurements. NWM and SFJ analyzed the results. NWM and OAN wrote the article. SFJ contributed to the interpretation of the findings and took the lead in revising the manuscript. NWM and SFJ approved the final version of the manuscript to be published.
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
There is no conflict of interest among the authors.
References
- [1]Chen L, Deng H, Cui H, Fang J, Zuo Z, Deng J, et al. Inflammatory responses and inflammationassociated diseases in organs. Oncotarget. 2018; 9(6): 7204-7218.
- [2]Libby P. Inflammatory mechanisms: the molecular basis of inflammation and disease. Nutrition reviews. 2007; 65(suppl_3): S140-S146.
- [3]Tiwari V. Burn wound: How it differs from other wounds? Indian journal of plastic surgery. 2012; 45(02): 364-373.
- [4]Srivastava S, Haider MF, Ahmad A, Ahmad U, Arif M and Ali A. Exploring Nanoemulsions for Prostate Cancer Therapy. Drug Research. 2021; 71(08): 417-428.
- [5]Moni A and Uddin MJ. Lipopolysaccharide tolerance attenuates inflammatory responses by increasing hemeoxygenase 1 and tristetraprolin expression in Raw264.7 macrophages. Journal of Advanced Biotechnology and Experimental Therapeutics. 2018; doi: 10.5455/jabet.d5.
- [6]Michels da Silva D, Langer H and Graf T. Inflammatory and molecular pathways in heart failure— ischemia, HFpEF and transthyretin cardiac amyloidosis. International journal of molecular sciences. 2019; 20(9): 2322
- [7]Lan Y-J, Sam NB, Cheng M-H, Pan H-F and Gao J. Progranulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Immune-Mediated Diseases. Journal of Inflammation Research. 2021; 14: 6543.
- [8]Abdolmaleki F, Kovanen PT, Mardani R, Gheibi-hayat SM, Bo S and Sahebkar A. Resolvins: Emerging players in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Clinical reviews in allergy & immunology. 2020; 58(1): 82-91.
- [9]Eriksen JL and Mackenzie IR. Progranulin: normal function and role in neurodegeneration. J Neurochem. 2008; 104(2): 287-97. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04968.x.
- [10]Nádró B, Lőrincz H, Juhász L, Szentpéteri A, Sztanek F, Varga É, et al. Determination of Serum Progranulin in Patients with Untreated Familial Hypercholesterolemia. Biomedicines. 2022; 10(4): 771.
- [11]Liu C-j and Bosch X. Progranulin: a growth factor, a novel TNFR ligand and a drug target. Pharmacology & therapeutics. 2012; 133(1): 124-132.
- [12]Fujii A, Mizutani YH, Kawamura M, Matusyama K, Mizutani Y, Shu E, et al. Serum progranulin level is a novel tool for monitoring disease activity of dermatomyositis with antimelanoma differentiationassociated protein 5 antibodies. Journal of Cutaneous Immunology and Allergy. 2021; 4(3): 50-56.
- [13]Lan YJ, Sam NB, Cheng MH, Pan HF and Gao J. Progranulin as a Potential Therapeutic Target in Immune-Mediated Diseases. J Inflamm Res. 2021; 14: 6543-6556.
- [14]Jian J, Li G, Hettinghouse A and Liu C. Progranulin: A key player in autoimmune diseases. Cytokine. 2018; 101: 48-55.
- [15]Richter J, Focke D, Ebert T, Kovacs P, Bachmann A, Lössner U, et al. Serum levels of the adipokine progranulin depend on renal function. Diabetes Care. 2013; 36(2): 410-4.
- [16]Nicoletto BB, Krolikowski TC, Crispim D and Canani LH. Serum and Urinary Progranulin in Diabetic Kidney Disease. PLoS One. 2016; 11(10): e0165177.
- [17]Qu H, Deng H and Hu Z. Plasma progranulin concentrations are increased in patients with type 2 diabetes and obesity and correlated with insulin resistance. Mediators Inflamm. 2013; 2013: 360190.
- [18]Edelman MJ, Feliciano J, Yue B, Bejarano P, Ioffe O, Reisman D, et al. GP88 (progranulin): a novel tissue and circulating biomarker for non-small cell lung carcinoma. Hum Pathol. 2014; 45(9): 1893-9.
- [19]Özgeris FB, Koçak Ö F, Kurt N, Parlak E, Yüce N and Keles MS. High Serum Progranulin Levels in COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study. Biochemistry (Mosc). 2022; 87(3): 207-214.
- [20]Cerezo LA, Kuklová M, Hulejová H, Vernerová Z, Kaspříková N, Veigl D, et al. Progranulin Is Associated with Disease Activity in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2015; 2015: 740357.
- [21]Hooi JKY, Lai WY, Ng WK, Suen MMY, Underwood FE, Tanyingoh D, et al. Global Prevalence of Helicobacter pylori Infection: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Gastroenterology. 2017; 153(2): 420-429.
- [22]Wang H, Sun Y, Liu S, Yu H, Li W, Zeng J, et al. Upregulation of progranulin by Helicobacter pylori in human gastric epithelial cells via p38MAPK and MEK1/2 signaling pathway: role in epithelial cell proliferation and migration. FEMS Immunol Med Microbiol. 2011; 63(1): 82-92. doi: 10.1111/j.1574- 695X.2011.00833.x.
- [23]Ren Z, Li J, Du X, Shi W, Guan F, Wang X, et al. Helicobacter pylori-Induced Progranulin Promotes the Progression of the Gastric Epithelial Cell Cycle by Regulating CDK4. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022; 32(7): 844-854.
- [24]Gong Y, Zhan T, Li Q, Zhang G, Tan B, Yang X, et al. Serum progranulin levels are elevated in patients with chronic hepatitis B virus infection, reflecting viral load. Cytokine. 2016; 85: 26-29.
- [25]Zhao YP, Tian QY, Frenkel S and Liu CJ. The promotion of bone healing by progranulin, a downstream molecule of BMP-2, through interacting with TNF/TNFR signaling. Biomaterials. 2013; 34(27): 6412-21. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.05.030.
- [26]Yamamoto Y, Takemura M, Serrero G, Hayashi J, Yue B, Tsuboi A, et al. Increased serum GP88 (Progranulin) concentrations in rheumatoid arthritis. Inflammation. 2014; 37(5): 1806-1813.
- [27]Arechavaleta-Velasco F, Perez-Juarez CE, Gerton GL and Diaz-Cueto L. Progranulin and its biological effects in cancer. Medical Oncology. 2017; 34(12): 1-11.
- [28]Tanimoto R, Lu KG, Xu S-Q, Buraschi S, Belfiore A, Iozzo RV, et al. Mechanisms of progranulin action and regulation in genitourinary cancers. Frontiers in Endocrinology. 2016; 7: 100.
- [29]Koo DH, Park CY, Lee ES, Ro J and Oh SW. Progranulin as a prognostic biomarker for breast cancer recurrence in patients who had hormone receptor-positive tumors: a cohort study. PLoS One. 2012; 7(6): e39880. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0039880.
- [30]Monami G, Gonzalez EM, Hellman M, Gomella LG, Baffa R, Iozzo RV, et al. Proepithelin promotes migration and invasion of 5637 bladder cancer cells through the activation of ERK1/2 and the formation of a paxillin/FAK/ERK complex. Cancer research. 2006; 66(14): 7103-7110.
- [31]Greither T, Fischer K and Theil G. Expression of GP88 (Progranulin) in serum of prostate cancer patients is associated with gleason scores and overall survival. 2018doi: 10.2147/cmar.S172069.
- [32]Liu C, Li J, Shi W, Zhang L, Liu S, Lian Y, et al. Progranulin Regulates Inflammation and Tumor. Antiinflamm Antiallergy Agents Med Chem. 2020; 19(2): 88-102.
- [33]He Z, Ong CH, Halper J and Bateman A. Progranulin is a mediator of the wound response. Nat Med. 2003; 9(2): 225-9.
- [34]Baillet A, Gossec L, Paternotte S, Etcheto A, Combe B, Meyer O, et al. Evaluation of serum interleukin-6 level as a surrogate marker of synovial inflammation and as a factor of structural progression in early rheumatoid arthritis: results from a French national multicenter cohort. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2015; 67(7): 905-12.
- [35]Liu BM, Martins TB, Peterson LK and Hill HR. Clinical significance of measuring serum cytokine levels as inflammatory biomarkers in adult and pediatric COVID-19 cases: A review. Cytokine. 2021; 142: 155478.
- [36]Feng Y, Ling Y, Bai T, Xie Y, Huang J, Li J, et al. COVID-19 with Different Severities: A Multicenter Study of Clinical Features. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020; 201(11): 1380-1388.